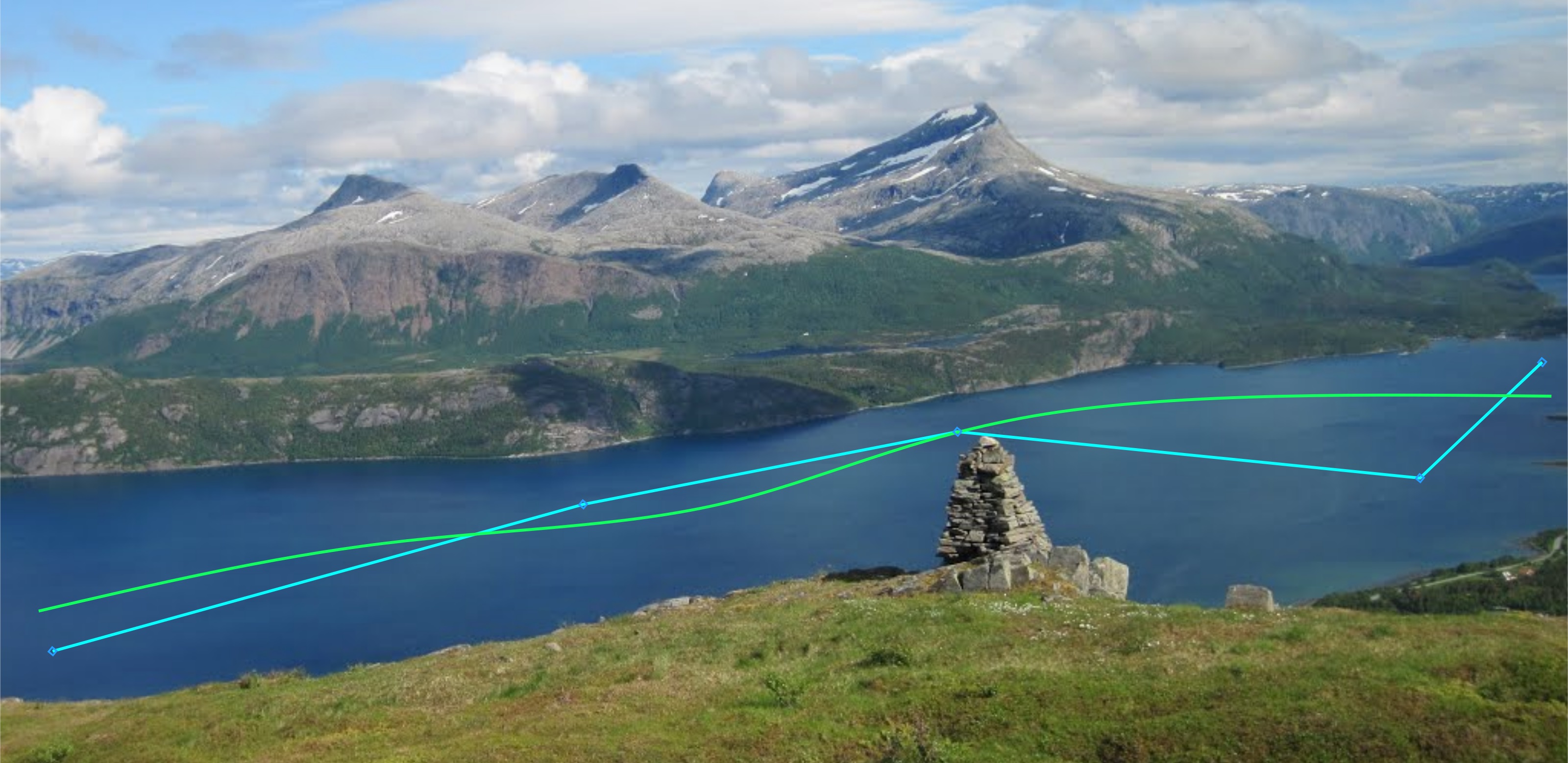

For surface vessels, several methods exist for path planning, and a main distinction is made between roadmap methods and complete-path optimization-based methods. The former uses some technique of adding waypoints to a map, and subsequently searches through the resulting graph for a feasible path. The latter generates a continuous smooth path through the environment, which is optimal with respect to some cost function and vehicle dynamics. A hierarchical overview is given in the figure below.
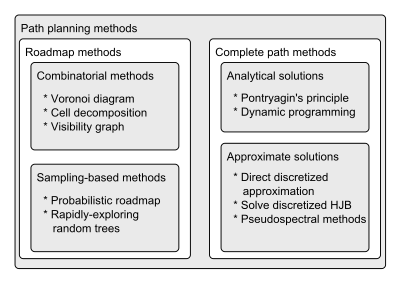
Roadmap methods are arguably simpler to implement and run faster than optimization-based methods, but it is believed that optimization-based methods may yield faster or more energy-effective paths. To evaluate whether the increased efficiency outweighs the increased complexity, it is necessary to quantify and compare the performances of these methods.
The candidate will perform a literature study during the project phase, and familiarize themselves with relevant software and hardware. Time permitting, they will also begin to work on the following suggested objectives, and continue with them in their master’s thesis:
- Perform background research on optimization-based and roadmap-based path planning methods
- Implement a framework for testing path planning methods using simulation
- Implement two or more path-planning methods, with at least one roadmap-based method and one optimization-based method
- Measure performance of the methods in terms of computational time, travel time, energy efficiency and robustness
- Discuss if it is favorable to change from roadmap-based methods to optimization-based methods
- Investigate the possibility of using optimal control to smooth roadmap-generated paths, and suggest other possible uses of optimal control in combination with roadmap methods
The candidate will cooperate closely with Kongsberg Maritime, and work with their autonomy controller “K-MATE.”
A starting point for the literature study is (Bitar, 2017), where several roadmap and optimization-based methods are reviewed. Additional information on path-planning methods is found in (Wolek, 2017) and (Roald, 2015).
Supervisor: Morten Breivik.
Co-supervisors: Rein Anders Apeland (Kongsberg Maritime) and Glenn Bitar.
References
Bitar, G. I. (2017). “Towards the Development of Autonomous Ferries.” MA thesis. NTNU.
Roald, A. L. (2015). “Path Planning for Vehicle Motion Control Using Numerical Optimization Methods.” MA thesis. NTNU.
Wolek, A. and C. A. Woolsey (2017). “Model-Based Path Planning.” In: Sensing and Control for Autonomous Vehicles. Ed. by T. I. Fossen, K. Y. Pettersen, and H. Nijmeijer. Springer International Publishing, pp. 183-206.